Wet method: large wet method, ammonia method, single alkali method, double alkali method, etc
Semi dry method: CFB circulating fluidized bed desulfurization, SDA rotary atomization desulfurization
Dry method: SDS baking soda desulfurization, fixed bed (moving bed) dry desulfurization
According to the flue gas parameters of the mine heat furnace, the wet and semi dry desulfurization process routes are not suitable for the desulfurization of mine heat furnace flue gas (combined with denitrification, comprehensive consideration is needed. If wet desulfurization is adopted, the subsequent denitrification will require too high temperature rise and energy consumption)
Based on practical experience, adopting a fixed bed (moving bed) dry desulfurization process route has low desulfurization efficiency and is prone to generating secondary dust pollution
In summary, the flue gas of the mine heating furnace adopts the SDS dry desulfurization process
Using sodium bicarbonate, the acid-base neutralization reaction involves a thermally activated pre reaction:
the freshly ground sodium bicarbonate powder comes into contact with the hot flue gas, and the small sodium bicarbonate particles quickly transform into sodium carbonate. The sodium carbonate produced by chemical pyrolysis has a high specific surface area (which can increase by more than 10 times)and porosity. Sodium car-bonate can quickly and effectively react with acidic gases, and during the process, acids(such as hydrochloric acid, sulfur dioxide, and hydrofluoric acid) are neutralized to achieve the goal of removing sulfur dioxide.
The main reaction equation is: 2NaHCO3(s)=Na2CO3(s)+H2O(g)+CO2(g)
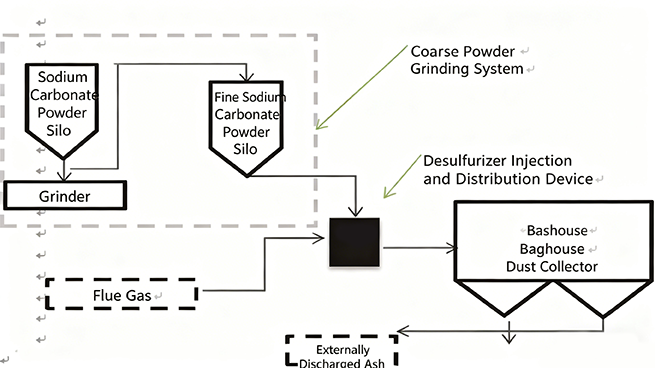
SDS desulfurization process diagram
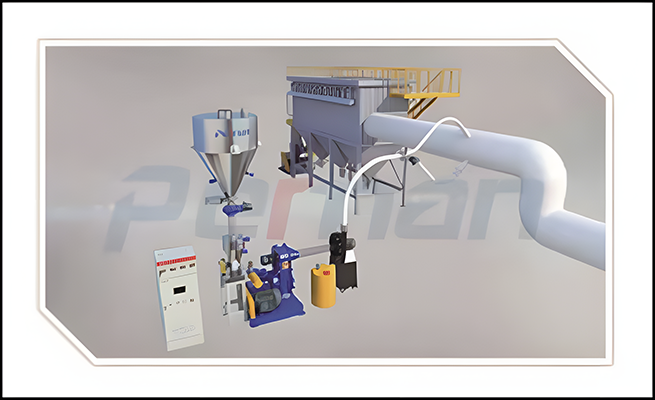

Due to the generation of desulfurization ash in the SDS desulfurization process, it needs to be collected using cloth bags, while the main furnace dust collector mainly collects micro silicon powder. The owner determines whether to use desulfurization ash and micro silicon powder together based on their own needs. As per the contract, only a first stage cloth bag dust collector is needed. If it needs to be separated, a second stage cloth bag needs to be used to collect desulfurization ash and micro silicon powder separately.
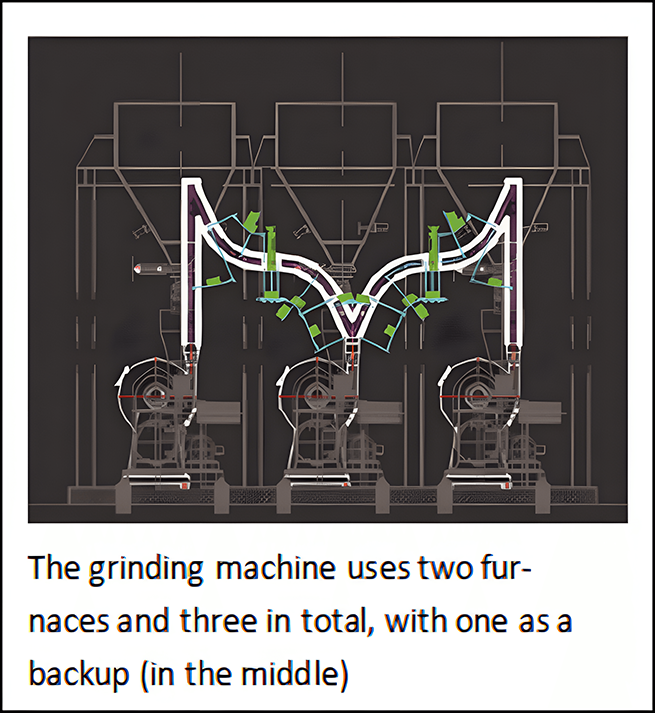
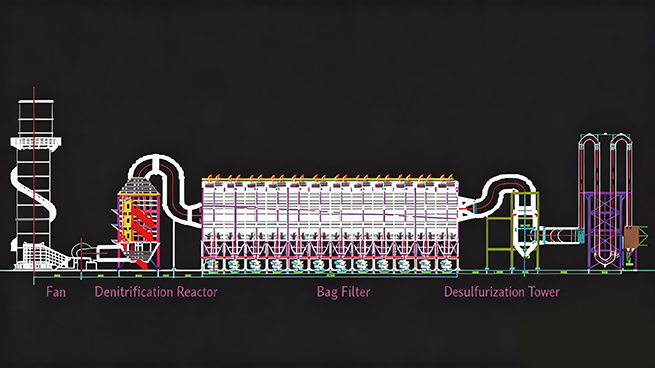
First-level bag dust removal design drawing
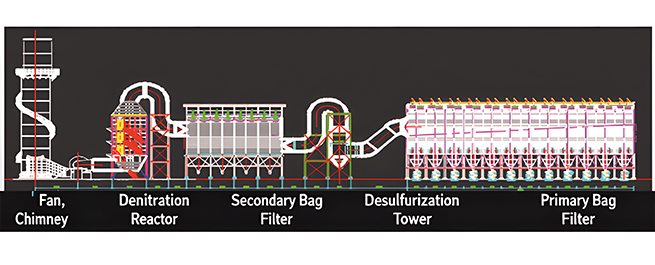
Secondary bag dust removal design drawing
Nitrogen oxides are produced during the high-temperature combustion of fossil fuels and air, and NOX includes NO, NO2, N20, N203, N204, N205, etc. The main pathways of generation include:
Thermal NOX: Nitrogen oxides produced by high-temperature oxidation of N2 in the combustion air.
Fuel type NOX: Fuel contains compounds containing nitrogen that are produced by oxidation during combustion. NOX is mainly composed of NO, accounting for over 90% of NOX (1.53).
Selective Non catalytic Reduction Technology (SNCR)
Selective catalytic reduction technology (SCR)
Joint Denitration Technology (SNCR+SCR) NOX control technology during combustion process (low nitrogen combustion)
Low excess air combustion
Air staged combustion and fuel staged combustion
Gas recirculation technology
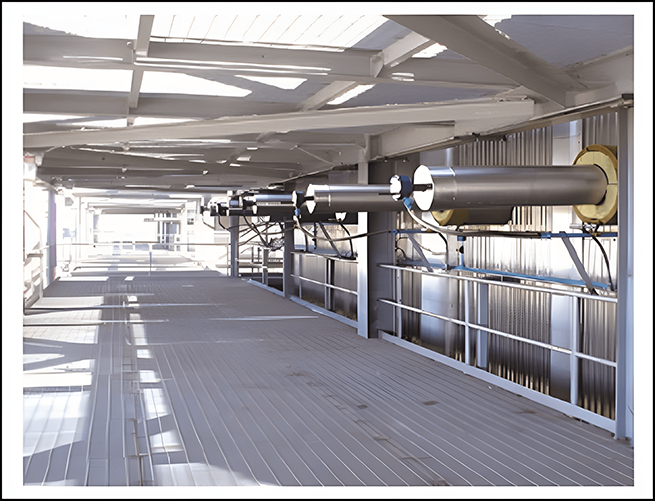
Key points of SCR denitrification process design
The flue gas temperature, mainly the active temperature of the catalyst
The content of sulfur dioxide in flue gas reacts with denitration reducing agents to form ammonium sulfate, which can affect the lifespan of catalysts
The selection and preparation of reducing agents mainly involve investment and operating costs
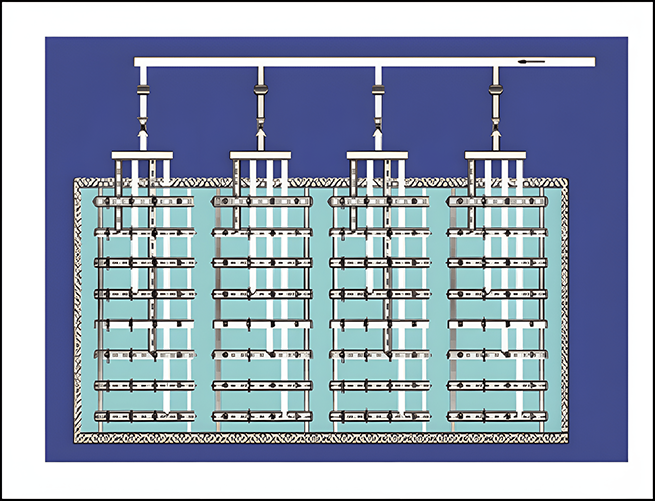
Ammonia spray system
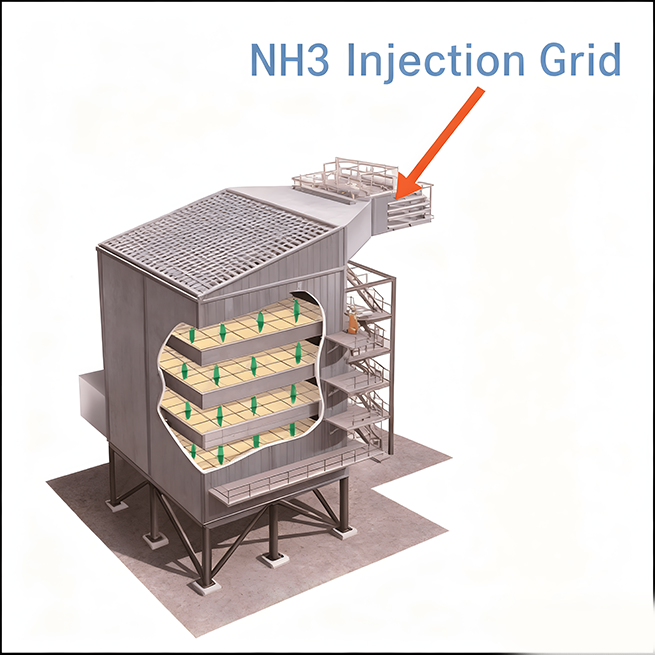
Ensure uniform mixing of ammonia and flue gas
Evenly distributed along the flue section
Soot blower-sonic soot blower


project | NOX control technology | Denitrification efficiency % | NOX control limit |
Low nitrogen combustion technology | Low nitrogen burner | 20-40 | Various low-nitrogen combustion technologies can be combined, and cannot meet ultra-low emission requirements |
Air grading | 20-40 | ||
Fuel grading combustion | 50-70 | ||
Flue gas recirculation | 10-30 | ||
Flue gas denitrification technology | SNCR | 40-60 | Unable to achieve ultra-low emissions |
SCR | 90 That's all | Can be ultra-low emissions |
Types of catalysts:
Honeycomb
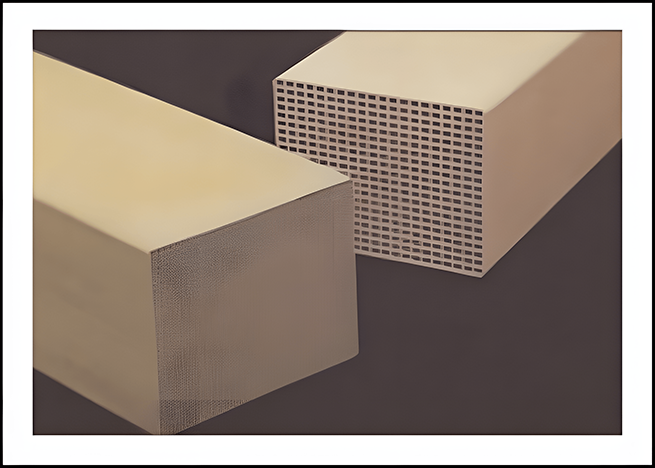
Plate type
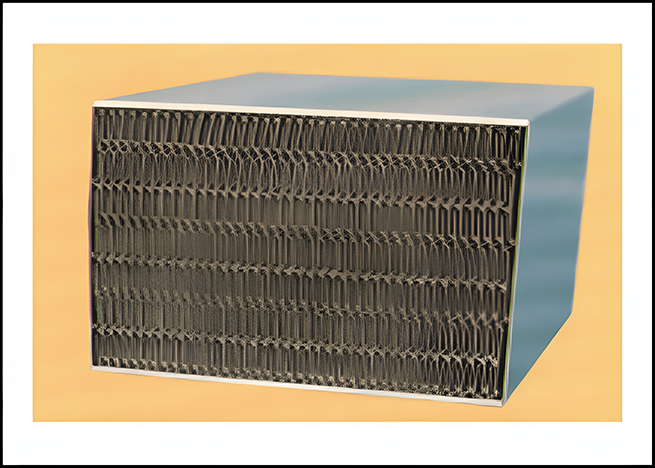
Corrugated plate type
Three-leaf clover

Easy to install
Short the time for catalyst to be removed from the reactor
Ammonia system (urea)hydrolysis process flow Hydrolysis includes: urea particle storage, urea dissolution, urea solution storage, hydrolysis system, product gas transportation, dilution air system.
Process description: Urea is discharged through a discharge system and dissolved in a tank, using desalinated water to produce a urea solution of 50-60%. The dissolved urea solution is transported to the urea solution storage tank. The urea solution with a concentration of 50-60% in the storage tank is transported to the ureahydrolysis reactor. The saturated steam is carried out through a coil in the hydrolysis reactor. The ammonia containing gas generated in the hydrolysis reactor enters the metering module and is diluted with dilution air
project | Liquid ammonia | ammonia | Urea |
Reactant cost | Cheap | More expensive | The most expensive |
Shipping costs | Cheap | expensive | Cheap |
Security | poisonous | harmful | harmless |
Store spare parts | high pressure | Regular pressure | Normal pressure dry state |
Storage method | Liquid | Liquid | Particulate |
First investment | Cheap | expensive | expensive |
Operating costs | Cheap, evaporate ammonia | Expensive, requiring high-calorie evaporation water and ammonia | Expensive, requiring high calorie hydrolysis of urea and evaporation of ammonia |
Equipment safety requirements | There are legal provisions | need | Basically not needed |
reducing agent | materials | Hourly consumption | Unit price of material(Yuan/ton) | Operating fee(Yuan/H) | Remark |
Desulfurizing agent | baking soda | 150KG/H | 3200 | 480 | The calculated price fluctuates according to market |
Denitrogen | 20% ammonia | 80KG/H | 800 | 64 | |
50% urea aqueous solution | 75KG/H | 1400 | 105 |
Unloading compressor
Ammonia storage tank
Ammonia evaporation tank
Ammonia buffer tank
Ammonia dilution tank
Waste water tank
Accessories such as pipelines and valves
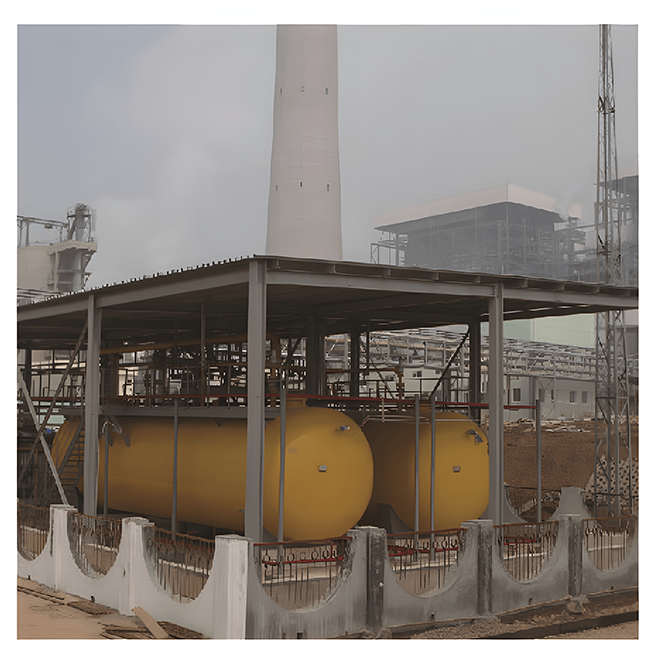


Ammonia discharge pump
Ammonia storage tank
Ammonia water transfer pump
Ammonia evaporator
Ammonia dilution tank
Waste water tank
Accessories such as pipelines and valves